Cart Pole#
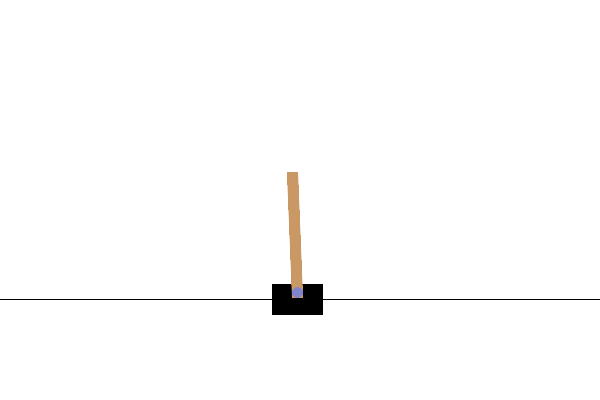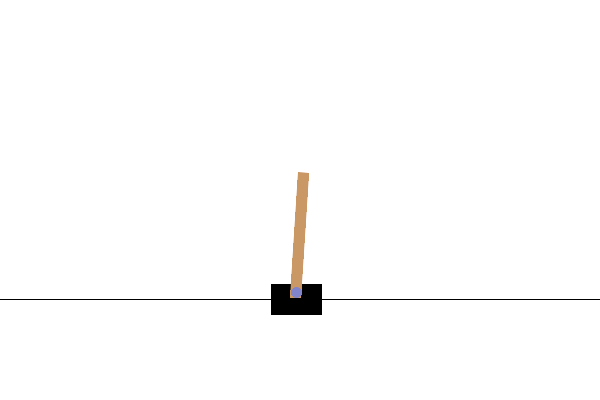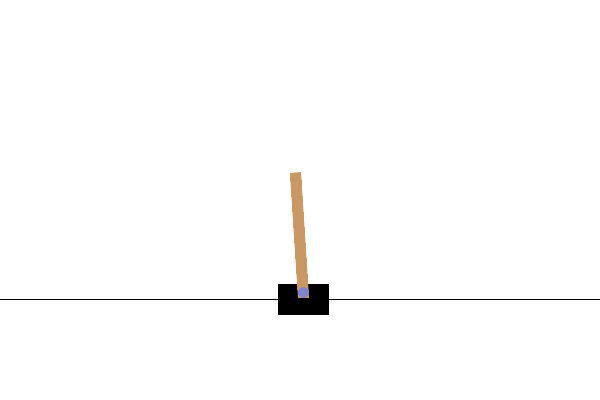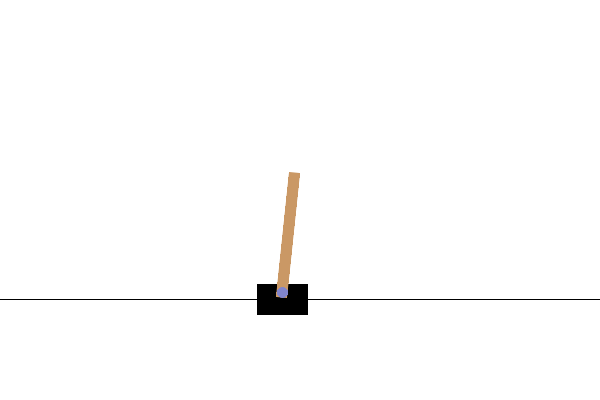
This environment is part of the Classic Control environments which contains general information about the environment.
Action Space |
|
Observation Space |
|
import |
|
Description#
This environment corresponds to the version of the cart-pole problem described by Barto, Sutton, and Anderson in “Neuronlike Adaptive Elements That Can Solve Difficult Learning Control Problem”. A pole is attached by an un-actuated joint to a cart, which moves along a frictionless track. The pendulum is placed upright on the cart and the goal is to balance the pole by applying forces in the left and right direction on the cart.
Action Space#
The action is a ndarray with shape (1,) which can take values {0, 1} indicating the direction
of the fixed force the cart is pushed with.
0: Push cart to the left
1: Push cart to the right
Note: The velocity that is reduced or increased by the applied force is not fixed and it depends on the angle the pole is pointing. The center of gravity of the pole varies the amount of energy needed to move the cart underneath it
Observation Space#
The observation is a ndarray with shape (4,) with the values corresponding to the following positions and velocities:
Num |
Observation |
Min |
Max |
|---|---|---|---|
0 |
Cart Position |
-4.8 |
4.8 |
1 |
Cart Velocity |
-Inf |
Inf |
2 |
Pole Angle |
~ -0.418 rad (-24°) |
~ 0.418 rad (24°) |
3 |
Pole Angular Velocity |
-Inf |
Inf |
Note: While the ranges above denote the possible values for observation space of each element, it is not reflective of the allowed values of the state space in an unterminated episode. Particularly:
The cart x-position (index 0) can be take values between
(-4.8, 4.8), but the episode terminates if the cart leaves the(-2.4, 2.4)range.The pole angle can be observed between
(-.418, .418)radians (or ±24°), but the episode terminates if the pole angle is not in the range(-.2095, .2095)(or ±12°)
Rewards#
Since the goal is to keep the pole upright for as long as possible, a reward of +1 for every step taken,
including the termination step, is allotted. The threshold for rewards is 500 for v1 and 200 for v0.
Starting State#
All observations are assigned a uniformly random value in (-0.05, 0.05)
Episode End#
The episode ends if any one of the following occurs:
Termination: Pole Angle is greater than ±12°
Termination: Cart Position is greater than ±2.4 (center of the cart reaches the edge of the display)
Truncation: Episode length is greater than 500 (200 for v0)
Arguments#
Cartpole only has render_mode as a keyword for gymnasium.make.
On reset, the options parameter allows the user to change the bounds used to determine the new random state.
>>> import gymnasium as gym
>>> env = gym.make("CartPole-v1", render_mode="rgb_array")
>>> env
<TimeLimit<OrderEnforcing<PassiveEnvChecker<CartPoleEnv<CartPole-v1>>>>>
>>> env.reset(seed=123, options={"low": -0.1, "high": 0.1}) # default low=-0.05, high=0.05
(array([ 0.03647037, -0.0892358 , -0.05592803, -0.06312564], dtype=float32), {})
Vectorized environment#
To increase steps per seconds, users can use a custom vector environment or with an environment vectorizor.
>>> import gymnasium as gym
>>> envs = gym.make_vec("CartPole-v1", num_envs=3, vectorization_mode="vector_entry_point")
>>> envs
CartPoleVectorEnv(CartPole-v1, num_envs=3)
>>> envs = gym.make_vec("CartPole-v1", num_envs=3, vectorization_mode="sync")
>>> envs
SyncVectorEnv(CartPole-v1, num_envs=3)


