Pusher¶
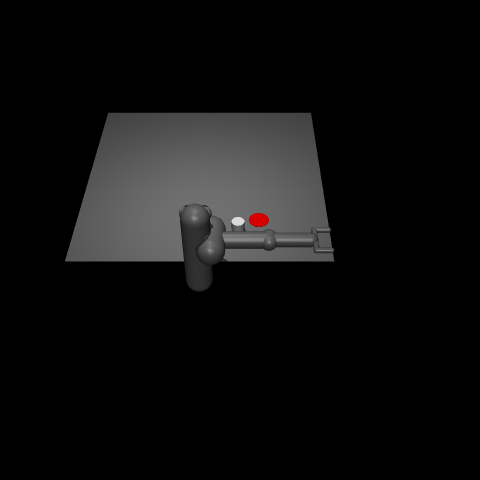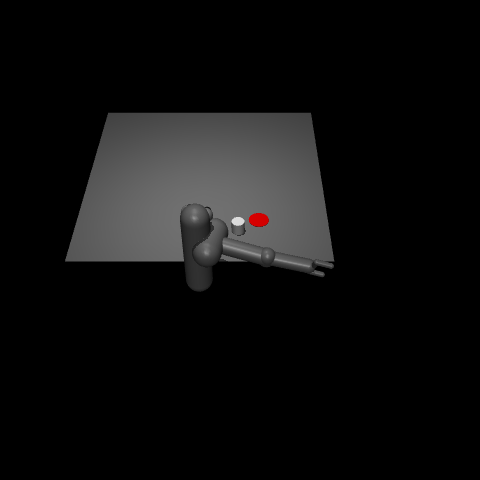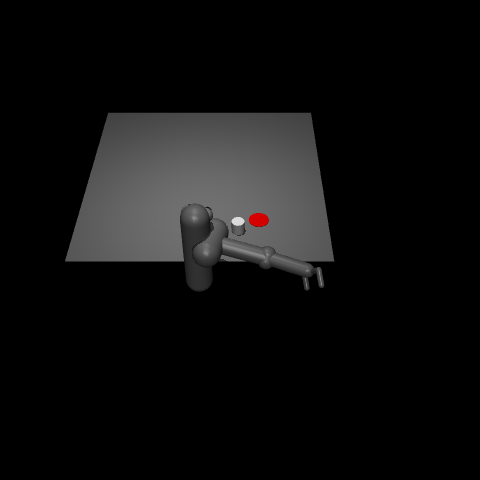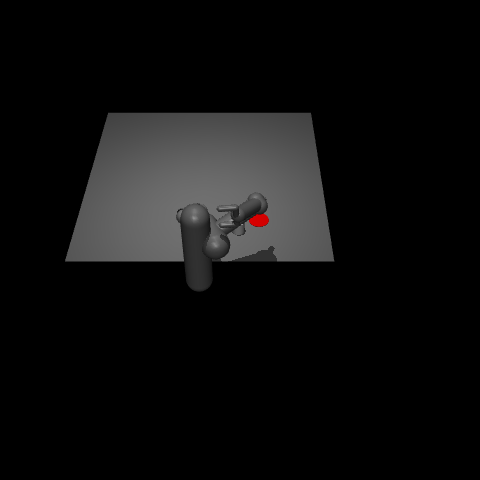
This environment is part of the Mujoco environments which contains general information about the environment.
Action Space |
|
Observation Space |
|
import |
|
Description¶
“Pusher” is a multi-jointed robot arm that is very similar to a human arm. The goal is to move a target cylinder (called object) to a goal position using the robot’s end effector (called fingertip). The robot consists of shoulder, elbow, forearm and wrist joints.
Action Space¶
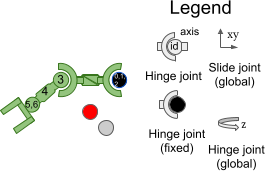
The action space is a Box(-2, 2, (7,), float32). An action (a, b) represents the torques applied at the hinge joints.
Num |
Action |
Control Min |
Control Max |
Name (in corresponding XML file) |
Joint |
Type (Unit) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 |
Rotation of the panning the shoulder |
-2 |
2 |
r_shoulder_pan_joint |
hinge |
torque (N m) |
1 |
Rotation of the shoulder lifting joint |
-2 |
2 |
r_shoulder_lift_joint |
hinge |
torque (N m) |
2 |
Rotation of the shoulder rolling joint |
-2 |
2 |
r_upper_arm_roll_joint |
hinge |
torque (N m) |
3 |
Rotation of hinge joint that flexed the elbow |
-2 |
2 |
r_elbow_flex_joint |
hinge |
torque (N m) |
4 |
Rotation of hinge that rolls the forearm |
-2 |
2 |
r_forearm_roll_joint |
hinge |
torque (N m) |
5 |
Rotation of flexing the wrist |
-2 |
2 |
r_wrist_flex_joint |
hinge |
torque (N m) |
6 |
Rotation of rolling the wrist |
-2 |
2 |
r_wrist_roll_joint |
hinge |
torque (N m) |
Observation Space¶
The observation space consists of the following parts (in order):
qpos (7 elements): Position values of the robot’s body parts.
qvel (7 elements): The velocities of these individual body parts (their derivatives).
xpos (3 elements): The coordinates of the fingertip of the pusher.
xpos (3 elements): The coordinates of the object to be moved.
xpos (3 elements): The coordinates of the goal position.
The observation space is a Box(-Inf, Inf, (17,), float64) where the elements are as follows:
Num |
Observation |
Min |
Max |
Name (in corresponding XML file) |
Joint |
Type (Unit) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 |
Rotation of the panning the shoulder |
-Inf |
Inf |
r_shoulder_pan_joint |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
1 |
Rotation of the shoulder lifting joint |
-Inf |
Inf |
r_shoulder_lift_joint |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
2 |
Rotation of the shoulder rolling joint |
-Inf |
Inf |
r_upper_arm_roll_joint |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
3 |
Rotation of hinge joint that flexed the elbow |
-Inf |
Inf |
r_elbow_flex_joint |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
4 |
Rotation of hinge that rolls the forearm |
-Inf |
Inf |
r_forearm_roll_joint |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
5 |
Rotation of flexing the wrist |
-Inf |
Inf |
r_wrist_flex_joint |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
6 |
Rotation of rolling the wrist |
-Inf |
Inf |
r_wrist_roll_joint |
hinge |
angle (rad) |
7 |
Rotational velocity of the panning the shoulder |
-Inf |
Inf |
r_shoulder_pan_joint |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
8 |
Rotational velocity of the shoulder lifting joint |
-Inf |
Inf |
r_shoulder_lift_joint |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
9 |
Rotational velocity of the shoulder rolling joint |
-Inf |
Inf |
r_upper_arm_roll_joint |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
10 |
Rotational velocity of hinge joint that flexed the elbow |
-Inf |
Inf |
r_elbow_flex_joint |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
11 |
Rotational velocity of hinge that rolls the forearm |
-Inf |
Inf |
r_forearm_roll_joint |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
12 |
Rotational velocity of flexing the wrist |
-Inf |
Inf |
r_wrist_flex_joint |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
13 |
Rotational velocity of rolling the wrist |
-Inf |
Inf |
r_wrist_roll_joint |
hinge |
angular velocity (rad/s) |
14 |
x-coordinate of the fingertip of the pusher |
-Inf |
Inf |
tips_arm |
slide |
position (m) |
15 |
y-coordinate of the fingertip of the pusher |
-Inf |
Inf |
tips_arm |
slide |
position (m) |
16 |
z-coordinate of the fingertip of the pusher |
-Inf |
Inf |
tips_arm |
slide |
position (m) |
17 |
x-coordinate of the object to be moved |
-Inf |
Inf |
object (obj_slidex) |
slide |
position (m) |
18 |
y-coordinate of the object to be moved |
-Inf |
Inf |
object (obj_slidey) |
slide |
position (m) |
19 |
z-coordinate of the object to be moved |
-Inf |
Inf |
object |
cylinder |
position (m) |
20 |
x-coordinate of the goal position of the object |
-Inf |
Inf |
goal (goal_slidex) |
slide |
position (m) |
21 |
y-coordinate of the goal position of the object |
-Inf |
Inf |
goal (goal_slidey) |
slide |
position (m) |
22 |
z-coordinate of the goal position of the object |
-Inf |
Inf |
goal |
sphere |
position (m) |
To understand the state space, an analogy can be drawn to a human arm, where the words “flex” and “roll” have the same meaning as in human joints.
Rewards¶
The total reward is: reward = reward_dist + reward_ctrl + reward_near.
reward_dist: This reward is a measure of how far the object is from the target goal position, with a more negative value assigned if the object is further away from the target. It is \(-w_{dist} \|(P_{object} - P_{target})\|_2\). where \(w_{dist}\) is the
reward_dist_weight(default is \(1\)).reward_ctrl: A negative reward to penalize the pusher for taking actions that are too large. It is measured as the negative squared Euclidean norm of the action, i.e. as \(-w_{control} \|action\|_2^2\). where \(w_{control}\) is the
reward_control_weight(default is \(0.1\)).reward_near: This reward is a measure of how far the fingertip of the pusher (the unattached end) is from the object, with a more negative value assigned for when the pusher’s fingertip is further away from the target. It is \(-w_{near} \|(P_{fingertip} - P_{target})\|_2\). where \(w_{near}\) is the
reward_near_weight(default is \(0.5\)).
info contains the individual reward terms.
Starting State¶
The initial position state of the Pusher arm is \(0_{6}\). The initial position state of the object is \(\mathcal{U}_{[[-0.3, -0.2], [0, 0.2]]}\). The position state of the goal is (permanently) \([0.45, -0.05, -0.323]\). The initial velocity state of the Pusher arm is \(\mathcal{U}_{[-0.005 \times I_{6}, 0.005 \times I_{6}]}\). The initial velocity state of the object is \(0_2\). The velocity state of the goal is (permanently) \(0_3\).
where \(\mathcal{U}\) is the multivariate uniform continuous distribution.
Note that the initial position state of the object is sampled until its distance to the goal is \( > 0.17 m\).
The default frame rate is 5, with each frame lasting 0.01, so dt = 5 * 0.01 = 0.05.
Episode End¶
Termination¶
The Pusher never terminates.
Truncation¶
The default duration of an episode is 100 timesteps.
Arguments¶
Pusher provides a range of parameters to modify the observation space, reward function, initial state, and termination condition.
These parameters can be applied during gymnasium.make in the following way:
import gymnasium as gym
env = gym.make('Pusher-v5', xml_file=...)
Parameter |
Type |
Default |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
str |
|
Path to a MuJoCo model |
|
float |
|
Weight for reward_near term (see |
|
float |
|
Weight for reward_dist term (see |
|
float |
|
Weight for reward_control term (see |
Version History¶
v5:
Minimum
mujocoversion is now 2.3.3.Fixed bug: increased the density of the object to be higher than air (related GitHub issue).
Added
default_camera_configargument, a dictionary for setting themj_cameraproperties, mainly useful for custom environments.Added
frame_skipargument, used to configure thedt(duration ofstep()), default varies by environment check environment documentation pages.Added
xml_fileargument.Fixed bug:
reward_distance&reward_nearwas based on the state before the physics step, now it is based on the state after the physics step (related GitHub issue).Added
reward_near_weight,reward_dist_weight,reward_control_weightarguments to configure the reward function (defaults are effectively the same as inv4).Fixed
info["reward_ctrl"]not being multiplied by the reward weight.Added
info["reward_near"]which is equal to the reward termreward_near.
v4: All MuJoCo environments now use the MuJoCo bindings in mujoco >= 2.1.3.
Warning: This version of the environment is not compatible with
mujoco>=3.0.0(related GitHub issue).
v3: This environment does not have a v3 release. Moved to the gymnasium-robotics repo.
v2: All continuous control environments now use mujoco-py >= 1.50. Moved to the gymnasium-robotics repo.
v1: max_time_steps raised to 1000 for robot based tasks (not including pusher, which has a max_time_steps of 100). Added reward_threshold to environments.
v0: Initial versions release.


